The carbon equivalent calculation takes into account the global warming potential of each greenhouse gas, compared to carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon equivalent allows for a more accurate comparison of emissions of different greenhouse gases.
As mentioned in the previously published article, in order to convert the other gases into CO2and, the GWP (Global Warming Potential) was developed. And for your information, below are listed the GWP values of each GHG (the CO molecule)2 will always have a GWP index equal to 1):

This is equivalent to saying that methane (CH4) has a potential to cause damage to the environment 28 times greater than CO2, that is, emitting 1 ton of methane has the same effect as emitting 28 tons of CO2. Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) has a damage potential 23,500 times greater than CO2, that is, emitting just 1 ton of Sulfur Hexafluoride into the atmosphere is equivalent to emitting 23,500 tons of CO2, in terms of impact on the greenhouse effect.
However, there is still one more part of the calculation that needs attention. Although CO2 have a GWP factor of 1.1 tonnes of CO2 is equivalent to only 0.2727 tons of Carbon Equivalent. This is because the calculation of Carbon Equivalent only considers the mass of the Carbon atom (C) contained in the CO molecule.2, comprising only 27.27% of the total mass of the molecule. Thus, the Carbon Equivalent is calculated through the value of the relative GWP multiplied by 0.2727, as shown in the table below:
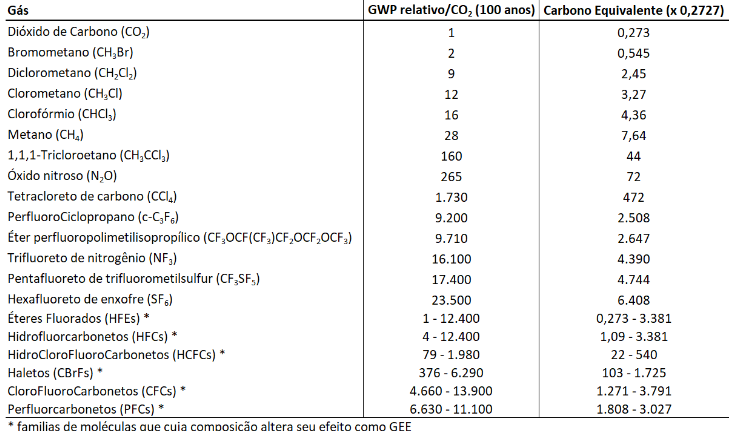
In this way, it is possible to understand how a sale works in the carbon market: Suppose that 1 ton of Carbon Equivalent is quoted at 1,000 dollars in the market. In this way, the removal of 1 ton of CO2 from the atmosphere would allow the generation of 0.273 carbon credits, with a value of 273 dollars, while the removal of 1 ton of Sulfur Hexafluoride would allow the generation of 6.4 carbon credits, worth a total of 6,408 dollars.
Thus, the formula for calculating carbon equivalent is the multiplication of the mass quantity of a gas (mg, g, kg or tons) by its GWP factor, multiplied by the factor of 0.2727 and, finally, converted to tons, since 1 carbon credit is paid for each ton of CO2and.
According to analyses by the World Agroforestry Center (ICRAF) together with the Amazon Initiative Consortium (IA), to measure and account for the carbon equivalent, it is necessary to follow the following main steps:
- Identify sources of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions;
- Measure the amounts of GHG emitted;
- Calculate the carbon equivalent (CO2e);
- Record and monitor emissions regularly.
Therefore, measuring carbon equivalent is essential to understanding and addressing the impact of human activities on the environment and to implementing effective measures to reduce it. In addition, it is an important tool for transparency, accountability and awareness of the need for sustainable actions.
Carbon equivalent accounting allows for the accurate quantification of these emissions, enabling the identification of the most significant sources and the implementation of effective measures to reduce them. This is crucial for achieving sustainability goals, both at a global and local level, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the negative effects of global warming.









One Response
Good Afternoon, Dear All! I have some questions: 1) How much is 1 ton of CO2 capable of destroying the Ozone layer? 2) What is the size of the Ozone layer that protects planet Earth? 3) What is the % that has already been destroyed from the Ozone layer?