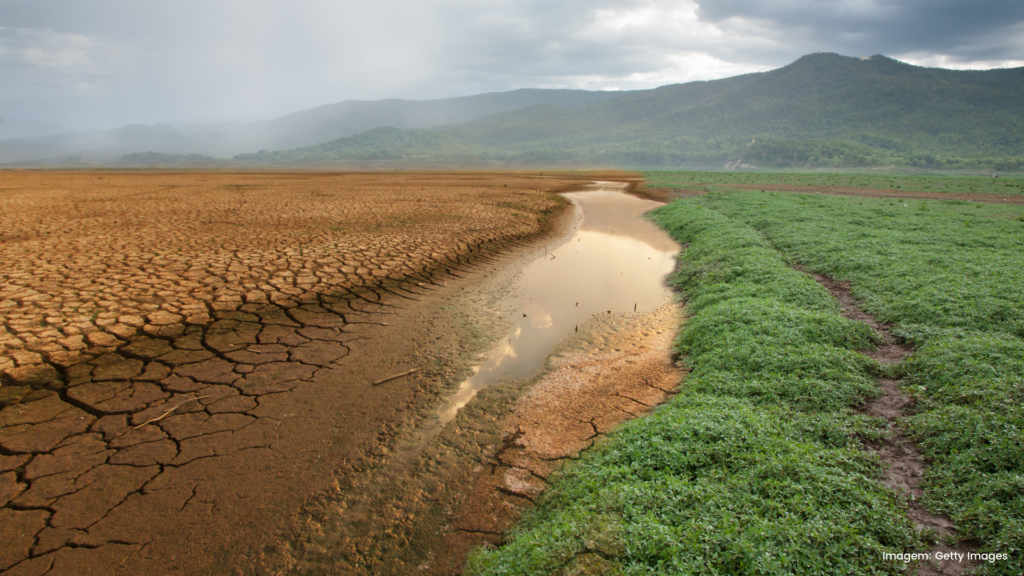
The impact of changes caused by a natural event that negatively alters the lives of human beings and the environment is the simplest definition of climate risk. There are two fundamental risk factors:
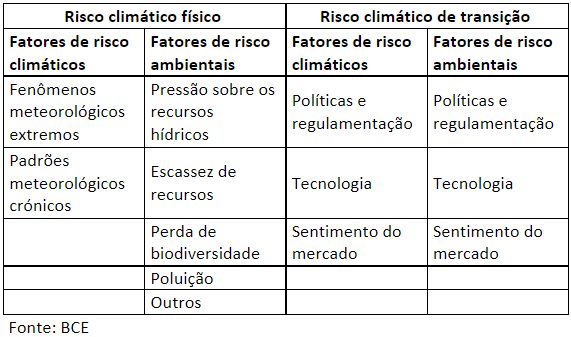
Physical Climate Risk: It refers to material, human, biodiversity, water and water resources, soil, air pollution, environmental degradation, deforestation, among other losses. It is categorized as acute when it results from extreme climate events and as chronic when it results from progressive climate events.
Transition Climate Risk: It refers to the losses of an institution that may result from the adjustment process in the search for environmentally sustainable development and decarbonization.
The issue of climate risk is so important that the Central Bank of Brazil (BC) issued the CMN RESOLUTION No. 4,943, OF SEPTEMBER 15, 2021, where among other things it also presents in Art. 38-C. your definition of climate risk:
I – transition climate risk: possibility of losses for the institution caused by events associated with the transition process to a low-carbon economy, in which greenhouse gas emissions are reduced or offset and the natural mechanisms for capturing these gases are preserved; and
II – physical climate risk: possibility of losses occurring to the institution caused by events associated with frequent and severe weather or long-term environmental changes, which may be related to changes in climate patterns.
In practice, some banks are now required to measure and report the climate risks of their operations from December 1, 2022, which directly impacts any banking transaction that companies need to carry out with banks. In practice, everyone will need to measure and calculate the climate risks of their processes so that banks can calculate the climate risks of their operations.








